11. Momentum & Impulse
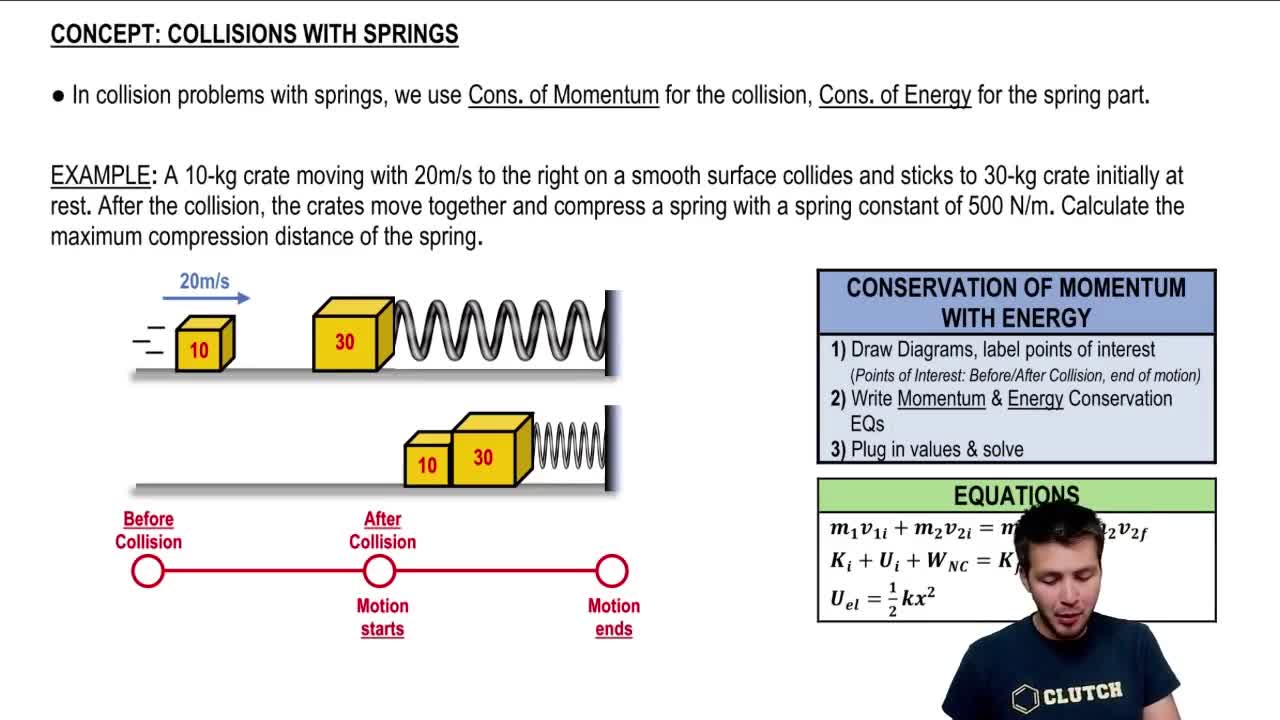
Collisions with Springs
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
An 8g piece of sticky clay strikes and embeds itself in a 0.992kg block at rest on a frictionless, horizontal surface. The block is attached to a spring with a spring constant of 5N/m. The impact compresses the spring 75.0 cm. What was the initial speed of the clay?
1081views18rank - Textbook Question
One end of a massless, 30-cm-long spring with spring constant 15 N/m is attached to a 250 g stationary air-track glider; the other end is attached to the track. A 500 g glider hits and sticks to the 250 g glider, compressing the spring to a minimum length of 22 cm. What was the speed of the 500 g glider just before impact?
1291views1rank - Textbook Question
A 600 g air-track glider collides with a spring at one end of the track. FIGURE EX11.13 shows the glider's velocity and the force exerted on the glider by the spring. How long is the glider in contact with the spring?
1506views - Textbook Question
A bullet of mass m = 0.0010 kg embeds itself in a wooden block with mass M = 0.999 kg, which then compresses a spring (k = 140 N/m) by a distance 𝓍 = 0.050 m before coming to rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and table is μ = 0.50. What fraction of the bullet’s initial kinetic energy is dissipated (in damage to the wooden block, rising temperature, etc.) in the collision between the bullet and the block?
673views - Textbook Question
A bullet of mass m = 0.0010 kg embeds itself in a wooden block with mass M = 0.999 kg, which then compresses a spring (k = 140 N/m) by a distance 𝓍 = 0.050 m before coming to rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and table is μ = 0.50. What is the initial velocity (assumed horizontal) of the bullet?
455views