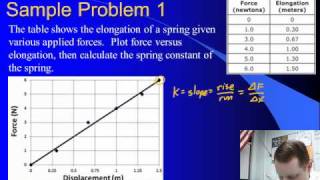
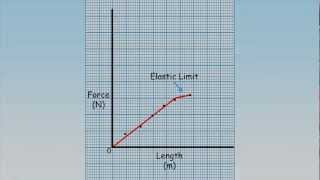
7. Friction, Inclines, Systems
Intro to Springs (Hooke's Law)
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
A vertical spring is originally 60 cm long. When you attach a 5 kg object to it, the spring stretches to 70 cm.
(a) Find the force constant on the spring.
(b) You now attach an additional 10 kg to the spring. Find its new length.(For the multiple choice selection, answer only part (b). Use g=10 m/s2.)
1238views22rank2comments - Textbook Question
A spring of equilibrium length L₁ and spring constant k₁ hangs from the ceiling. Mass m₁ is suspended from its lower end. Then a second spring, with equilibrium length L₂ and spring constant k₂, is hung from the bottom of m₁. Mass m₂ is suspended from this second spring. How far is m₂ below the ceiling?
1150views - Textbook Question
A 30 g mass is attached to one end of a 10-cm-long spring. The other end of the spring is connected to a frictionless pivot on a frictionless, horizontal surface. Spinning the mass around in a circle at 90 rpm causes the spring to stretch to a length of 12 cm. What is the value of the spring constant?
2064views - Textbook Question
A 10-cm-long spring is attached to the ceiling. When a 2.0 kg mass is hung from it, the spring stretches to a length of 15 cm. How long is the spring when a 3.0 kg mass is suspended from it?
1750views - Textbook Question
A 12 kg weather rocket generates a thrust of 200 N. The rocket, pointing upward, is clamped to the top of a vertical spring. The bottom of the spring, whose spring constant is 550 N/m, is anchored to the ground. Initially, before the engine is ignited, the rocket sits at rest on top of the spring. How much is the spring compressed?
1152views - Multiple Choice
When a spring is compressed, which form of energy increases?
66views - Multiple Choice
According to Hooke's Law, how does an elastic material exert an elastic force when it is stretched or compressed?
55views - Multiple Choice
If the spring constant of a spring is doubled, what happens to the extension produced by a given force according to Hooke's Law ?
52views