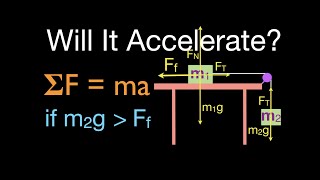
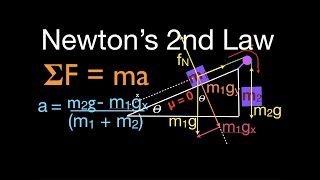
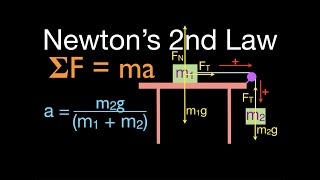
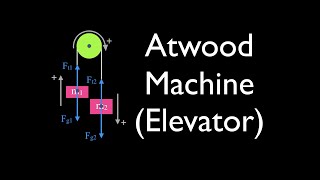
6. Intro to Forces (Dynamics)
Forces in Connected Systems of Objects
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceThe three ropes shown in the figure are tied to a steel ring. Two of the ropes are anchored to walls at right angles, and the third rope pulls as shown. If the tension in rope 2 is , what is the mass of the steel ring?1129views
- Multiple ChoiceThree blocks are placed in line on a frictionless table with block B in between blocks A and C. Block A has a mass of , block B has a mass of , and block C has a mass of . A student pushes horizontally on block A with a force of . What is the magnitude of the force of block B on block C?1904views1comments
- Multiple ChoiceThe coefficient of kinetic friction for block A in the figure is 0.2 and the pulley is frictionless. If the mass of block A is , what is the magnitude of its acceleration?1718views
- Multiple ChoiceA toy train consists of an engine, followed by a boxcar, followed by a caboose. All have mass m. When the engine's wheels provide a force F in the forward direction, the train has acceleration a. What is the magnitude of the force of the boxcar on the caboose? Ignore any frictional effects.1275views
- Textbook Question
A 75-kg petty thief wants to escape from a third-story jail window. Unfortunately, a makeshift rope made of sheets tied together can support a mass of only 62 kg. How might the thief use this 'rope' to escape? Give a quantitative answer.
1107views - Textbook Question
A window washer pulls herself upward using the bucket–pulley apparatus shown in Fig. 4–40. If she increases this force by 15%, what will her acceleration be? The mass of the person plus the bucket is 78 kg.
<Image>
1002views - Textbook Question
(II) One 3.2-kg paint bucket is hanging by a massless cord from another 3.2-kg paint bucket, also hanging by a massless cord, as shown in Fig. 4–41. If the buckets are at rest, what is the tension in each cord?
1107views1comments - Textbook Question
III) Determine a formula for the magnitude of the force exerted on the large block (mC) in Fig. 4–56 so that the mass mA does not move relative to mC. Ignore all friction. Assume mB does not make contact with mC.
1016views