19. Fluid Mechanics
Pressure Gauge: Barometer
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
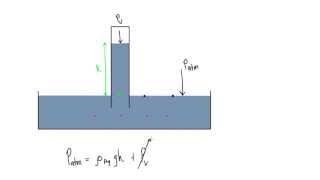
A classic barometer (shown below) is built with a 1.0-m tall glass tube and filled with mercury (13,600 kg/m3). Calculate the atmospheric pressure, in ATM, surrounding the barometer if the column of liquid is 76 cm high. (Use g=9.8 m/s2.)
1191views9rank - Textbook Question
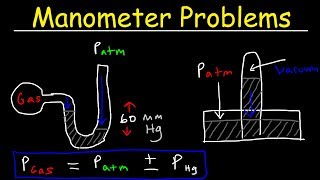
The liquid in the open-tube manometer in Fig. 12.8a is mercury, y1=3.00 cm,and y2=7.00 cm. Atmospheric pressure is 980 millibars. What is (a) the absolute pressure at the bottom of the U-shaped tube; (b) the absolute pressure in the open tube at a depth of 4.00 cm below the free surface; (c) the absolute pressure of the gas in the container; (d) the gauge pressure of the gas in pascals?
1396views - Textbook Question
A house at the bottom of a hill is fed by a full tank of water 6.0 m deep and connected to the house by a pipe that is 75 m long at an angle of 61° from the horizontal (Fig. 13–53). How high could the water shoot if it came vertically out of a broken pipe in front of the house?
823views - Textbook Question
Determine the minimum gauge pressure needed in the water pipe leading into a building if water is to come out of a faucet on the fourteenth floor, 44 m above that pipe.
689views - Textbook Question
A 3.2-N force is applied to the plunger of a hypodermic needle. If the diameter of the plunger is 1.3 cm and that of the needle is 0.20 mm, with what force does the fluid leave the needle?
741views - Multiple Choice
What does a falling barometric reading (, atmospheric pressure) typically indicate?
67views - Multiple Choice
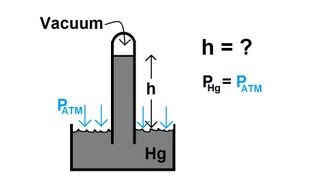
Which statement best describes how a barometer works to measure atmospheric pressure?
66views - Multiple Choice
Which principle explains how a barometer measures atmospheric pressure?
54views