30. Induction and Inductance
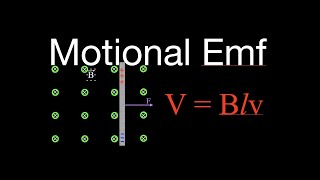
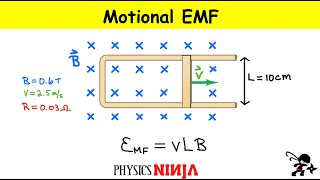
Motional EMF
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
A thin rod moves in a perpendicular, unknown magnetic field. If the length of the rod is 10 cm and the induced EMF is 1 V when it moves at 5 m/s, what is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
1541views26rank - Textbook Question
INT A 20-cm-long, zero-resistance slide wire moves outward, on zero-resistance rails, at a steady speed of 10 m/s in a 0.10 T magnetic field. (See Figure 30.26.) On the opposite side, a 1.0 Ω carbon resistor completes the circuit by connecting the two rails. The mass of the resistor is 50 mg. How much force is needed to pull the wire at this speed?
136views - Textbook Question
A potential difference of 0.050 V is developed across the 10-cm-long wire of FIGURE EX30.3 as it moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to the figure. What are the strength and direction (in or out) of the magnetic field?
1285views - Textbook Question
INT A 10-cm-long wire is pulled along a U-shaped conducting rail in a perpendicular magnetic field. The total resistance of the wire and rail is 0.20 Ω. Pulling the wire at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s causes 4.0 W of power to be dissipated in the circuit. How big is the pulling force?
1151views - Textbook Question
A 22.0-cm-diameter coil consists of 36 turns of circular copper wire 2.6 mm in diameter. A uniform magnetic field, perpendicular to the plane of the coil, changes at a rate of 8.65 x 10-3 T/s. Determine (a) the current in the loop, and (b) the rate at which thermal energy is produced.
809views - Multiple Choice
A conducting rod of length moves with constant velocity perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude . What is the magnitude of the motional emf induced in the rod?
66views