30. Induction and Inductance
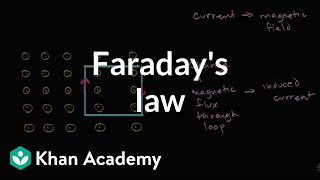
Faraday's Law
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
A tightly-wound 200-turn rectangular loop has dimensions of 40cm by 70cm. A constant magnetic field of 3.5T points in the same direction as the normal of the loop. If the dimensions of the loop change to 20cm by 35cm over 0.5s, with the number of turns remaining the same, what is the induced EMF on the rectangular loop?
1565views32rank5comments - Multiple Choice
A square conducting wire of side length 4 cm is in a 2 T magnetic field. It rotates such that the angle of the magnetic field to the normal of the square increases from 30° to 60° in 2 s. What is the induced current on the wire if its resistance is 5 mΩ?
1554views19rank5comments - Multiple Choice
The figure shows a wire loop being moved toward a current-carrying wire. If the loop continues to move past the wire, so that the loop is lower than the wire in the picture, and still moving, what will be the direction of the induced current in the loop?1391views1rank - Multiple ChoiceIn a region of space, a magnetic field is increasing at. A square loop of wire with a side of is oriented perpendicular to the field. The loop has a total resistance of. What current is induced in the loop?1332views
- Textbook Question
A long, straight solenoid with a cross-sectional area of 8.00 cm2 is wound with 90 turns of wire per centimeter, and the windings carry a current of 0.350 A. A second winding of 12 turns encircles the solenoid at its center. The current in the solenoid is turned off such that the magnetic field of the solenoid becomes zero in 0.0400 s. What is the average induced emf in the second winding?
2499views1rank - Textbook Question
The magnetic field B at all points within the colored circle shown in Fig. E29.15 has an initial magnitude of 0.750 T. (The circle could represent approximately the space inside a long, thin solenoid.) The magnetic field is directed into the plane of the diagram and is decreasing at the rate of -0.0350 T/s. If the ring is cut at some point and the ends are separated slightly, what will be the emf between the ends?
<Image>
1180views - Textbook Question
The magnetic field B at all points within the colored circle shown in Fig. E29.15 has an initial magnitude of 0.750 T. (The circle could represent approximately the space inside a long, thin solenoid.) The magnetic field is directed into the plane of the diagram and is decreasing at the rate of -0.0350 T/s. What is the shape of the field lines of the induced electric field shown in Fig. E29.15 , within the colored circle?
<Image>
1145views - Textbook Question
A long, thin solenoid has 400 turns per meter and radius 1.10 cm. The current in the solenoid is increasing at a uniform rate di/dt. The induced electric field at a point near the center of the solenoid and 3.50 cm from its axis is 8.00 × 10-6 V/m. Calculate di/dt.
1930views1rank