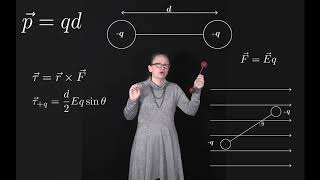24. Electric Force & Field; Gauss' Law
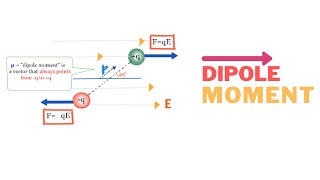
Dipole Moment
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Textbook Question
An electric dipole with dipole moment is in a uniform external electric field . Show that for the stable orientation in part (b), the dipole's own electric field tends to oppose the external field. Note: Part (b) asked which of the orientations in part (a) is stable, and which is unstable? (Hint: Consider a small rotation away from the equilibrium position and see what happens.) Also, part (a) asked to find the orientations of the dipole for which the torque on the dipole is zero.
1593views - Textbook Question
An electric dipole with dipole moment is in a uniform external electric field . Which of the orientations in part (a) is stable, and which is unstable? (Hint: Consider a small rotation away from the equilibrium position and see what happens.) Note: Part (a) asked to find the orientations of the dipole for which the torque on the dipole is zero.
1919views - Textbook Question
An electric dipole with dipole moment is in a uniform external electric field . Find the orientations of the dipole for which the torque on the dipole is zero.
2205views - Textbook Question
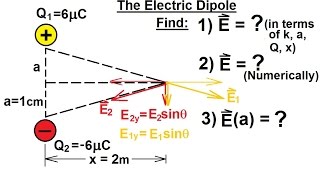
Point charges nC and nC are separated by mm, forming an electric dipole. The charges are in a uniform electric field whose direction makes an angle of ° with the line connecting the charges. What is the magnitude of this field if the torque exerted on the dipole has magnitude Nm?
2144views2rank - Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes an electric dipole?
59views - Multiple Choice
An electric dipole consists of two charges of equal magnitude separated by a distance . What is the magnitude of its dipole moment?
48views