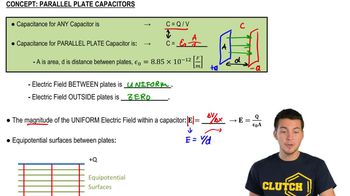
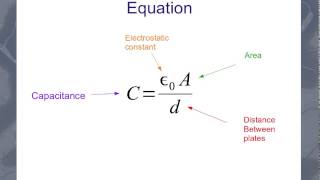
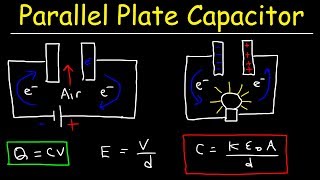
26. Capacitors & Dielectrics
Parallel Plate Capacitors
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Two circular plates of radius 2cm are brought together so their separation is 5mm. What is the capacitance of these plates?
1973views30rank1comments - Multiple Choice
A 3 F capacitor is given a potential difference across its plates of 10 V. What is the charge built up on its plates? If the source of the potential difference across the plates is removed, but the plates maintain their charge, what is the new potential difference across the capacitor if the distance between the plates is doubled?
1978views33rank3comments - Multiple ChoiceWhat is the smallest possible capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor with plate area separated by a distance , if you can fill it with any of the materials listed in Table 21.3?1149views1rank
- Multiple ChoiceOne gallon of typical gasoline has 132 MJ of energy. You wish to store that much energy in a parallel-plate capacitor for an electric car. Assume you charge the capacitor using a power source. You can fill the capacitor with any of the materials listed in Table 21.3, but the spacing between plates has to be 0.080 mm. What is the minimum surface area required for the capacitor? This may help to understand challenges in engineering electric cars.923views
- Textbook Question
A parallel-plate air capacitor is to store charge of magnitude pC on each plate when the potential difference between the plates is V.
(a) If the area of each plate is cm2, what is the separation between the plates?
(b) If the separation between the two plates is double the value calculated in part (a), what potential difference is required for the capacitor to store charge of magnitude pC on each plate?
1829views - Textbook Question
A -F parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a V battery. After the capacitor is fully charged, the battery is disconnected without loss of any of the charge on the plates.
(a) A voltmeter is connected across the two plates without discharging them. What does it read?
(b) What would the voltmeter read if (i) the plate separation were doubled; (ii) the radius of each plate were doubled but their separation was unchanged?
2163views1rank - Textbook Question
A parallel-plate air capacitor of capacitance pF has a charge of magnitude C on each plate. The plates are mm apart.
(a) What is the potential difference between the plates?
(b) What is the area of each plate?
(c) What is the electric field magnitude between the plates?
(d) What is the surface charge density on each plate?
983views - Textbook Question
The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor are mm apart, and each carries a charge of magnitude nC. The plates are in vacuum. The electric field between the plates has a magnitude of V/m. What is (a) the potential difference between the plates; (b) the area of each plate; (c) the capacitance?
1050views