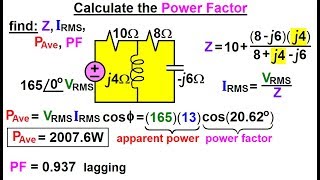
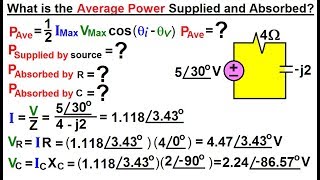
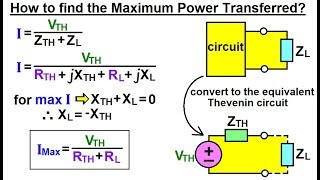
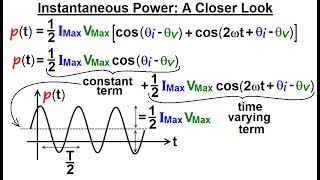
31. Alternating Current
Power in AC Circuits
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Textbook Question
A resistor with R = 300 Ω and an inductor are connected in series across an ac source that has voltage amplitude 500 V. The rate at which electrical energy is dissipated in the resistor is 286 W. What is (a) the impedance Z of the circuit; (b) the amplitude of the voltage across the inductor; (c) the power factor?
1525views - Textbook Question
The power of a certain CD player operating at 120 V rms is 20.0 W. Assuming that the CD player behaves like a pure resistor, find the maximum instantaneous power.
965views - Textbook Question
In an L-R-C series circuit, the components have the following values: L = 20.0 mH, C = 140 nF, and R = 350 Ω.The generator has an rms voltage of 120 V and a frequency of 1.25 kHz. Determine (a) the power supplied by the generator and (b) the power dissipated in the resistor.
1237views - Textbook Question
An L-R-C series circuit with L = 0.120 H, R = 240 Ω, and C = 7.30 μF carries an rms current of 0.450 A with a frequency of 400 Hz. What are the phase angle and power factor for this circuit?
1161views