Differentiate the following terms. Which one is “hit and miss”—that is, does not add a specific gene to a cell?
a. protoplast fusion
b. gene gun
c. microinjection
d. electroporation
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Differentiate the following terms. Which one is “hit and miss”—that is, does not add a specific gene to a cell?
a. protoplast fusion
b. gene gun
c. microinjection
d. electroporation
The DNA probe, 3'-GGCTTA, will hybridize with which of the following?
a. 5'-CCGUUA
b. 5'-CCGAAT
c. 5'-GGCTTA
d. 3'-CCGAAT
e. 3'-GGCAAU
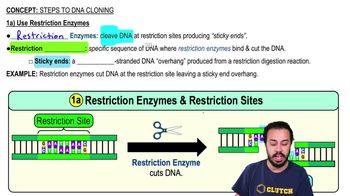
Some commonly used restriction enzymes are listed in Table 9.1.
a. Indicate which enzymes produce sticky ends.
b. Of what value are sticky ends in making rDNA?
The following enzymes are used to make cDNA. What is the second enzyme used to make cDNA?
a. reverse transcriptase
b. ribozyme
c. RNA polymerase
d. DNA polymerase
DRAW IT Identify and mark each of the following in making cDNA: transcription, RNA processing, reverse transcription, DNA polymerase, cDNA.
<IMAGE>
If you put a gene in a virus, the next step in genetic modification would be
a. insertion of a plasmid.
b. transformation.
c. transduction.
d. PCR.
e. Southern blotting.