Which of the following is the fourth basic step to genetically modify a cell?
a. transformation
b. ligation
c. plasmid cleavage
d. restriction-enzyme digestion of gene
e. isolation of gene
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Which of the following is the fourth basic step to genetically modify a cell?
a. transformation
b. ligation
c. plasmid cleavage
d. restriction-enzyme digestion of gene
e. isolation of gene
The following enzymes are used to make cDNA. What is the second enzyme used to make cDNA?
a. reverse transcriptase
b. ribozyme
c. RNA polymerase
d. DNA polymerase
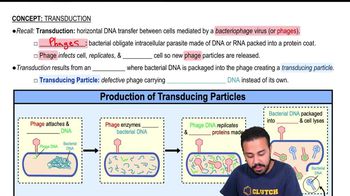
DRAW IT Identify and mark each of the following in making cDNA: transcription, RNA processing, reverse transcription, DNA polymerase, cDNA.
<IMAGE>
Describe an rDNA experiment in two or three sentences. Use the following terms: intron, exon, DNA, mRNA, cDNA, RNA polymerase, reverse transcriptase.
You are attempting to insert a gene for saltwater tolerance into a plant by using the Ti plasmid. In addition to the desired gene, you add a gene for tetracycline resistance (tet) to the plasmid. What is the purpose of the tet gene?
How does RNAi “silence” a gene?