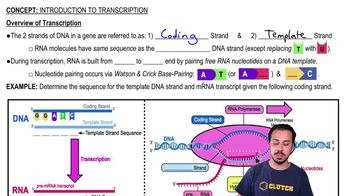
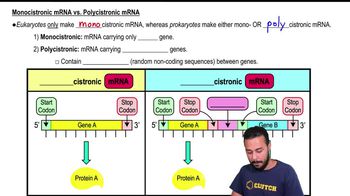
Two offspring cells are most likely to inherit which one of the following from the parent cell?
a. a change in a nucleotide in mRNA
b. a change in a nucleotide in tRNA
c. a change in a nucleotide in rRNA
d. a change in a nucleotide in DNA
e. a change in a protein