Match the following terms to the definitions in questions 1 and 2.
a. conjugation
b. transcription
c. transduction
d. transformation
e. translation
Transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient cell by a bacteriophage.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Match the following terms to the definitions in questions 1 and 2.
a. conjugation
b. transcription
c. transduction
d. transformation
e. translation
Transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient cell by a bacteriophage.
Which of the following is not a method of horizontal gene transfer?
a. binary fission
b. conjugation
c. integration of a transposon
d. transduction
e. transformation
Match the following terms to the definitions in questions 1 and 2.
a. conjugation
b. transcription
c. transduction
d. transformation
e. translation
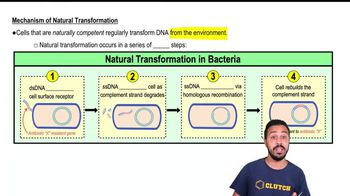
Transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient as naked DNA in solution.
Identify when (before transcription, after transcription but before translation, after translation) each of the following regulatory mechanisms functions.
a. ATP combines with an enzyme, altering its shape.
b. A short RNA is synthesized that is complementary to mRNA.
c. Methylation of DNA occurs.
d. An inducer combines with a repressor.
Plasmids differ from transposons in that plasmids
a. become inserted into chromosomes.
b. are self-replicated outside the chromosome.
c. move from chromosome to chromosome.
d. carry genes for antibiotic resistance.
e. none of the above
Use the following choices to answer questions 7 and 8:
a. catabolite repression
b. DNA polymerase
c. induction
d. repression
e. translation
Mechanism by which the presence of glucose inhibits the lac operon.