A decrease in the production of C3 would result in
a. increased susceptibility to infection.
b. increased numbers of white blood cells.
c. increased phagocytosis.
d. activation of C5 through C9.
e. none of the above
 Tortora 14th Edition
Tortora 14th Edition Ch. 16 - Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
Ch. 16 - Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Problem 16.8a
Problem 16.8a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

A decrease in the production of C3 would result in
a. increased susceptibility to infection.
b. increased numbers of white blood cells.
c. increased phagocytosis.
d. activation of C5 through C9.
e. none of the above
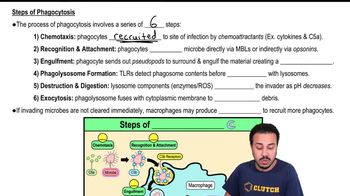
Give several examples of how microbes evade the complement system.
In 1884, Elie Metchnikoff observed cells collected around a splinter inserted in a sea star embryo. This was the discovery of
a. blood cells.
b. sea stars.
c. phagocytosis.
d. immunity.
e. none of the above
Helicobacter pylori uses the enzyme urease to counteract a chemical defense in the human organ in which it lives. This chemical defense is
a. lysozyme.
b. hydrochloric acid.
c. superoxide radicals.
d. sebum.
e. complement.
Are the following involved in innate or in adaptive immunity? Identify the role of each in immunity:
a. TLRs
b. transferrins
c. antimicrobial peptides
Which of the following statements about IFN- is false?
a. It interferes with viral replication.
b. It is host-cell–specific.
c. It is released by fibroblasts.
d. It is virus-specific.
e. It is released by lymphocytes.