In 1884, Elie Metchnikoff observed cells collected around a splinter inserted in a sea star embryo. This was the discovery of
a. blood cells.
b. sea stars.
c. phagocytosis.
d. immunity.
e. none of the above
 Tortora 14th Edition
Tortora 14th Edition Ch. 16 - Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
Ch. 16 - Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Problem 16.9a
Problem 16.9a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

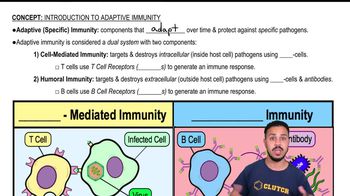
In 1884, Elie Metchnikoff observed cells collected around a splinter inserted in a sea star embryo. This was the discovery of
a. blood cells.
b. sea stars.
c. phagocytosis.
d. immunity.
e. none of the above
DRAW IT Label on the figure the following processes that result in phagocytosis: margination, diapedesis, adherence, and phagolysosome formation.
<IMAGE>
Helicobacter pylori uses the enzyme urease to counteract a chemical defense in the human organ in which it lives. This chemical defense is
a. lysozyme.
b. hydrochloric acid.
c. superoxide radicals.
d. sebum.
e. complement.
Which of the following statements about IFN- is false?
a. It interferes with viral replication.
b. It is host-cell–specific.
c. It is released by fibroblasts.
d. It is virus-specific.
e. It is released by lymphocytes.
How can a human make 100 billion different antibodies with only 25,000 different genes?
Classify the following vaccines by type. Which could cause the disease it is supposed to prevent?
a. attenuated measles virus
b. dead Rickettsia prowazekii
c. Vibrio cholerae toxoid
d. hepatitis B antigen produced in yeast cells
e. purified polysaccharides from Streptococcus pyogenes
f. H. influenzae polysaccharide bound to diphtheria toxoid
g. a plasmid containing genes for influenza A protein