Draw the Fischer projection of the C3 epimer of d-glucose. Compare your structure with those in Table 6.1 and give the name of this compound.
Ch.6 Carbohydrates–Life’s Sweet Molecules
Chapter 3, Problem 75b
Will the following carbohydrates produce a positive Benedict’s test?
(b) lactose
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that Benedict's test is used to identify reducing sugars, which have free aldehyde or ketone groups capable of reducing copper(II) ions to copper(I) oxide, resulting in a color change.
Recognize that lactose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and galactose linked by a β(1→4) glycosidic bond.
Determine if lactose has a free anomeric carbon that can open to form an aldehyde group, which is necessary for a positive Benedict's test.
Recall that in lactose, the glucose unit has a free anomeric carbon, allowing it to act as a reducing sugar.
Conclude that since lactose has a free anomeric carbon, it will produce a positive Benedict's test, indicating it is a reducing sugar.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Benedict's Test
Benedict's test is a qualitative assay used to detect reducing sugars in a solution. When a reducing sugar is present, the copper(II) ions in the Benedict's reagent are reduced to copper(I) oxide, resulting in a color change that can range from green to brick red, depending on the amount of sugar present. This test is commonly used in biochemistry to identify sugars like glucose and lactose.
Recommended video:
Guided course
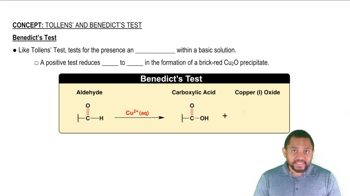
Benedict's Test Concept 3
Reducing Sugars
Reducing sugars are carbohydrates that can donate electrons to other molecules, thus reducing them. This property is due to the presence of a free aldehyde or ketone group in their structure. Common examples include glucose, fructose, and lactose, which can all participate in redox reactions, making them detectable by tests like Benedict's.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ketoses as Reducing Sugars Concept 2
Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar composed of glucose and galactose, commonly found in milk. It is classified as a reducing sugar because it has a free aldehyde group when in solution, allowing it to react with Benedict's reagent. Therefore, lactose will produce a positive result in a Benedict's test, indicating the presence of reducing sugars.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Types of Disaccharides Example 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
21
views
Textbook Question
Draw the Fischer projection of the product of reduction reaction of d-galactose at C1
6
views
Textbook Question
Will the following carbohydrates produce a positive Benedict’s test?
(a) d-glucose
8
views
Textbook Question
The glycosidic bond in a disaccharide was determined to be α (1→6) . Hydrolysis of the disaccharide produced one galactose and one fructose. Draw the structure of the disaccharide.
8
views
Textbook Question
ALLIED Health Our bodies cannot digest cellulose because we lack the enzyme cellulase. Why is cellulose an important part of a healthy diet if we cannot digest it?
4
views
Textbook Question
The shell of a shrimp is composed of chitin. If you eat a boiled shrimp without removing the shell, will your body break the shell down into its component sugars? Explain. (Hint: Compare chitin’s structure to that of amylose and cellulose.)
49
views
