Draw the Fischer projection of the product of reduction reaction of d-galactose at C1
Ch.6 Carbohydrates–Life’s Sweet Molecules
Chapter 3, Problem 80
The glycosidic bond in a disaccharide was determined to be α (1→6) . Hydrolysis of the disaccharide produced one galactose and one fructose. Draw the structure of the disaccharide.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the monosaccharides involved: Galactose and Fructose.
Understand the glycosidic linkage: An α (1→6) bond means the first carbon of one sugar is linked to the sixth carbon of the other sugar.
Draw the structure of galactose, ensuring the anomeric carbon (C1) is in the alpha configuration (OH group down).
Draw the structure of fructose, ensuring the C6 is available for bonding.
Connect the C1 of galactose to the C6 of fructose to form the α (1→6) glycosidic bond.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
7mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycosidic Bond
A glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that connects a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which can also be a carbohydrate. In disaccharides, this bond forms between the anomeric carbon of one sugar and a hydroxyl group of another, determining the structure and properties of the sugar. The notation α (1→6) indicates the specific carbons involved in the bond and its orientation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
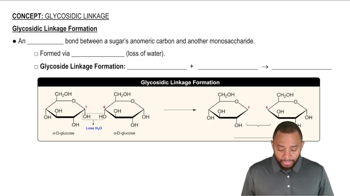
Glycosidic Linkage Formation Concept 1
Disaccharide Structure
A disaccharide is a carbohydrate composed of two monosaccharide units linked by a glycosidic bond. The specific arrangement of these units and the type of glycosidic bond influence the disaccharide's properties and how it is metabolized. In this case, the disaccharide consists of galactose and fructose, which are linked through an α (1→6) bond.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Types of Disaccharides Concept 1
Hydrolysis Reaction
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction that involves the breaking of a bond in a molecule using water. In the context of disaccharides, hydrolysis results in the separation of the two monosaccharide units, allowing them to exist independently. This reaction is essential for the digestion of carbohydrates, as it converts complex sugars into simpler forms that can be absorbed by the body.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Triacylglycerol Reactions: Hydrolysis Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
6
views
Textbook Question
Will the following carbohydrates produce a positive Benedict’s test?
(a) d-glucose
8
views
Textbook Question
Will the following carbohydrates produce a positive Benedict’s test?
(b) lactose
9
views
Textbook Question
ALLIED Health Our bodies cannot digest cellulose because we lack the enzyme cellulase. Why is cellulose an important part of a healthy diet if we cannot digest it?
4
views
Textbook Question
The shell of a shrimp is composed of chitin. If you eat a boiled shrimp without removing the shell, will your body break the shell down into its component sugars? Explain. (Hint: Compare chitin’s structure to that of amylose and cellulose.)
49
views
Textbook Question
Glycogen and amylopectin are both branched polymers of glucose. Read the descriptions of each in Section 6.6. Which molecule has a more compact structure? Explain.
9
views
