Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
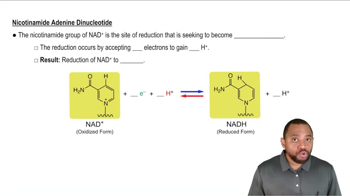
Dinucleotide Structure
A dinucleotide consists of two nucleotides linked together by a phosphodiester bond. Each nucleotide is made up of a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA), and a nitrogenous base (adenine in this case). Understanding the arrangement of these components is essential for accurately drawing the dinucleotide AT.
Recommended video:
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Concept 2
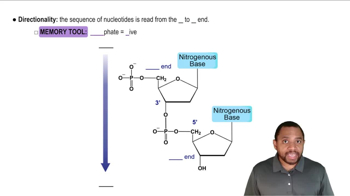
5' and 3' Ends
In nucleic acids, the 5' and 3' ends refer to the orientation of the sugar molecule in the nucleotide. The 5' end has a phosphate group attached to the fifth carbon of the sugar, while the 3' end has a hydroxyl group on the third carbon. Labeling these ends is crucial for understanding the directionality of DNA strands and their synthesis.
Recommended video:
Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids Concept 2
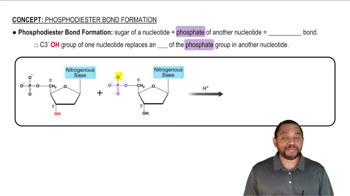
Phosphodiester Bond
A phosphodiester bond is a covalent bond that links the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the hydroxyl group on the sugar of another nucleotide. This bond forms the backbone of DNA and RNA, providing structural integrity and allowing for the formation of long chains of nucleotides. Identifying this bond is key to understanding how nucleotides connect in a dinucleotide.
Recommended video:
Phosphodiester Bond Formation Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance