Textbook Question
Describe the differences in the two ends of a nucleic acid.
17
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
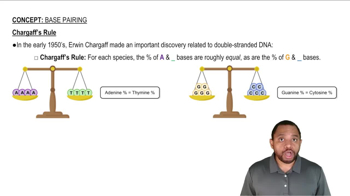

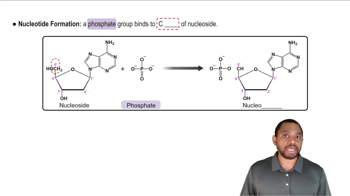
Describe the differences in the two ends of a nucleic acid.
Draw the dinucleotide AT that would be found in DNA. Label the 5' and 3' ends of your structure. Identify the phosphodiester bond.
Name the three types of RNA and their functions.
Identify each of the following as a purine or a pyrimidine:
a. guanine
The sequence of bases in a DNA template strand is 5'GGCTTATTGCCA3'. What is the corresponding mRNA produced?
Provide the three-letter amino acid sequence expected from each of the following mRNA segments: b. 5'UUU|CCC|UUU|CCC3'