An aqueous KNO3 solution is made using 72.5 g of KNO3 diluted to a total solution volume of 2.00 L. Calculate the molarity of the solution. (Assume a density of 1.05 g/mL for the solution.)
To what volume should you dilute 50.0 mL of a 5.00 M KI solution so that 25.0 mL of the diluted solution contains 3.05 g of KI?

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
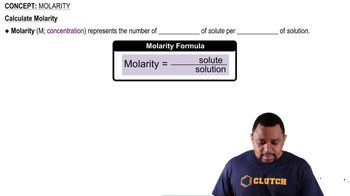
Molarity (M)
Dilution Equation

Mass to Moles Conversion

An aqueous KNO3 solution is made using 72.5 g of KNO3 diluted to a total solution volume of 2.00 L. Calculate the molality of the solution. (Assume a density of 1.05 g/mL for the solution.)
An aqueous KNO3 solution is made using 72.5 g of KNO3 diluted to a total solution volume of 2.00 L. Calculate the mass percent of the solution. (Assume a density of 1.05 g/mL for the solution.)
Silver nitrate solutions are often used to plate silver onto other metals. What is the maximum amount of silver (in grams) that can be plated out of 4.8 L of an AgNO3 solution containing 3.4% Ag by mass? Assume that the density of the solution is 1.01 g/mL.
A dioxin-contaminated water source contains 0.085% dioxin by mass. How much dioxin is present in 2.5 L of this water? Assume a density of 1.00 g/mL.
Lead is a toxic metal that affects the central nervous system. A Pb-contaminated water sample contains 0.0011% Pb by mass. How much of the water (in mL) contains 150 mg of Pb? (Assume a density of 1.0 g/mL.)
