Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. In the case of n-pentyne, which has the formula C5H10, isomers can be formed by varying the position of the triple bond within the carbon chain, leading to different structural formulas.
Recommended video:
Isomerism in Coordination Complexes Example
Alkynes
Alkynes are a class of hydrocarbons characterized by at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. n-Pentyne is a straight-chain alkyne with five carbon atoms. Understanding the properties and reactivity of alkynes is essential for predicting the behavior of their isomers and for drawing their structural formulas accurately.
Recommended video:
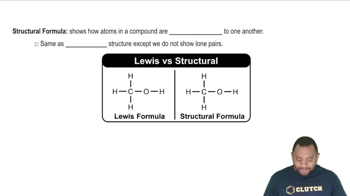
Structural Formula
A structural formula represents the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, showing how the atoms are bonded to each other. For isomers of n-pentyne, drawing the structural formulas involves indicating the position of the triple bond and ensuring that the carbon skeleton adheres to the rules of valency, which is crucial for visualizing the different isomeric forms.
Recommended video: