Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Structural Isomers
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms. This variation can lead to different physical and chemical properties. For octane (C8H18), there are 18 structural isomers, which can be categorized into straight-chain and branched forms, showcasing the diversity of molecular structures possible with the same number of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Recommended video:
Octane and Its Isomers
Octane is an alkane with eight carbon atoms, commonly represented by the formula C8H18. Its structural isomers include various arrangements of carbon atoms, such as straight chains and branched chains. Understanding the specific structural formulas of these isomers is crucial for applications in fields like organic chemistry and fuel science, where octane ratings are significant for gasoline performance.
Recommended video:
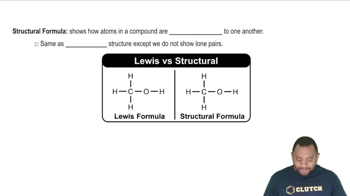
Drawing Structural Formulas
Drawing structural formulas involves representing the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, including bonds between them. For octane isomers, this means accurately depicting the carbon skeleton and the hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon. Familiarity with conventions such as line-angle formulas and the ability to visualize three-dimensional structures are essential skills for chemists when illustrating these isomers.
Recommended video: