Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Carboxylic Acids
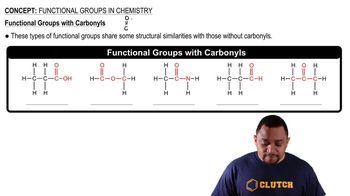
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more carboxyl groups (-COOH). This functional group consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (OH). Carboxylic acids are known for their acidic properties and are commonly found in various biological and industrial processes.
Recommended video:
Rules for Naming Carboxylic Acids
Ester Functional Group
Esters are derived from carboxylic acids and are formed when the hydroxyl group of the carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkoxy group (-O-R). The general structure of an ester can be represented as RCOOR', where R and R' are hydrocarbon chains. Esters are often characterized by their pleasant fragrances and are commonly used in flavorings and fragrances.
Recommended video:
Carbonyl Functional Groups
Structural Representation
Structural representation in chemistry involves depicting the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, including bonds and functional groups. For carboxylic acids and esters, this includes showing the carbon backbone and the specific functional groups. Understanding how to draw these structures is essential for visualizing molecular interactions and predicting chemical behavior.
Recommended video: