Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH). They are known for their acidic properties due to the ability of the carboxyl group to donate a proton (H+) in solution. This functional group is crucial in various chemical reactions, including esterification and neutralization with bases.
Recommended video:
Rules for Naming Carboxylic Acids
Neutralization Reaction
A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base to produce water and a salt. In this case, the carboxylic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base, resulting in the formation of a salt (sodium carboxylate) and water. This type of reaction is fundamental in acid-base chemistry and is often used in titrations.
Recommended video:
Lewis Dot Structures: Neutral Compounds
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Sodium hydroxide is a strong base commonly used in various chemical reactions, including neutralization and saponification. It dissociates completely in water to produce hydroxide ions (OH-), which can react with acids to form water and a salt. Understanding its role in reactions with carboxylic acids is essential for predicting the products of such reactions.
Recommended video:
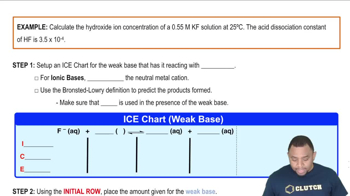
Hydroxide Ion Concentration Example

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance