Textbook Question
Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. e. 105.0 mL of 0.15 M CH3NH2; 95.0 mL of 0.10 M HCl
738
views


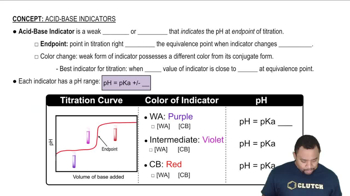

Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. e. 105.0 mL of 0.15 M CH3NH2; 95.0 mL of 0.10 M HCl
Blood is buffered by carbonic acid and the bicarbonate ion. Normal blood plasma is 0.024 M in HCO3- and 0.0012 M H2CO3 (pKa1 for H2CO3 at body temperature is 6.1).
a. What is the pH of blood plasma?
The fluids within cells are buffered by H2PO4- and HPO42- . b. Could a buffer system employing H3PO4 as the weak acid and H2PO4- as the weak base be used as a buffer system within cells? Explain.
Which buffer system is the best choice to create a buffer with pH = 9.00? For the best system, calculate the ratio of the masses of the buffer components required to make the buffer. HF/KF HNO2/KNO2 NH3/NH4Cl HClO/KClO