Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Buffer Systems
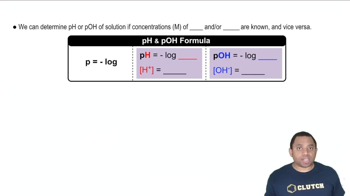
A buffer system is a solution that resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. It typically consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The effectiveness of a buffer is determined by its pKa and the concentrations of its components, which help maintain a stable pH in a specific range.
Recommended video:
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation relates the pH of a buffer solution to the pKa of the acid and the ratio of the concentrations of the conjugate base to the weak acid. It is expressed as pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]). This equation is essential for calculating the required ratio of buffer components to achieve a desired pH, such as 9.00 in this case.
Recommended video:
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
pKa and pH Relationship
The pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka) and indicates the strength of an acid in solution. A lower pKa value corresponds to a stronger acid. For effective buffering, the pH of the solution should be close to the pKa of the weak acid used in the buffer system, allowing for optimal resistance to pH changes.
Recommended video: