Textbook Question
Based on effective nuclear charge (Zeff), which ion is the strongest oxidizing agent?
(a) Cu2+
(b) Ni2+
(c) Fe2+
(d) Mn2+
105
views



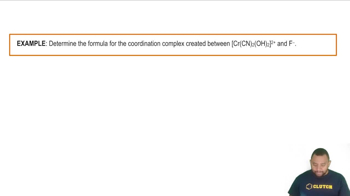
Based on effective nuclear charge (Zeff), which ion is the strongest oxidizing agent?
(a) Cu2+
(b) Ni2+
(c) Fe2+
(d) Mn2+
Look at the location in the periodic table of elements A, B, C, and D. What is the electron configuration of the transition metal in each of the following ions?
(a) A2+
(b) B+
The oxalate ion is a bidentate ligand as indicated in Figure 21.8. Would you expect the carbonate ion to be a monodentate or bidentate ligand? Explain your reasoning.
Predict the number of unpaired electrons for each of the following.
(c) Zn2+
(d) Cr3+
Predict the number of unpaired electrons for each of the following.
(c) Mn3+
(d) Cr2+
Predict the number of unpaired electrons for each of the following.
(a) Sc3+
(b) Co2+