The following pictures represent solutions that contain one or more of the compounds H2A, NaHA, and Na2A, where H2A is a weak diprotic acid. (Na+ ions and solvent water molecules have been omitted for clarity.)

(b) Which solution has the greatest buffer capacity?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
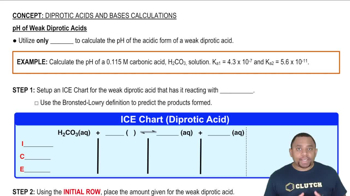
Key Concepts
Buffer Capacity

Weak Diprotic Acid
Equilibrium and Le Chatelier's Principle

The following pictures represent initial concentrations in solutions that contain a weak acid HA (pKa = 6.0) and its sodium salt NaA. (Na+ ions and solvent water molecules have been omitted for clarity.)
. (b) Draw a picture that represents the equilibrium state of solution (1) after the addition of two H3O+ ions.
The following pictures represent solutions that contain one or more of the compounds H2A, NaHA, and Na2A, where H2A is a weak diprotic acid. (Na+ ions and solvent water molecules have been omitted for clarity.)
(a) Which of the solutions are buffer solutions?
The following plot shows two pH titration curves, each representing the titration of 50.0 mL of 0.100 M acid with 0.100 M NaOH:
. (a) Which of the two curves represents the titration of a strong acid? Which represents a weak acid?
The following plot shows two pH titration curves, each representing the titration of 50.0 mL of 0.100 M acid with 0.100 M NaOH:
. (b) What is the approximate pH at the equivalence point for each of the acids?
The following plot shows two pH titration curves, each representing the titration of 50.0 mL of 0.100 M acid with 0.100 M NaOH:
. (c) What is the approximate pKa of the weak acid?
