Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Titration Curves
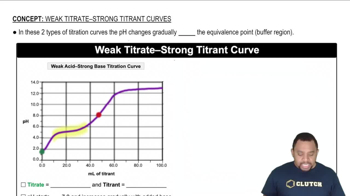
Titration curves graphically represent the change in pH of a solution as a titrant is added. The shape of the curve indicates the strength of the acid or base being titrated. A steep rise in pH indicates a strong acid or base, while a more gradual slope suggests a weak acid or base. The equivalence point, where the amount of titrant equals the amount of substance being titrated, is crucial for determining the strength of the acid or base.
Recommended video:
Acid-Base Titration Curves
Strong vs. Weak Acids
Strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), completely dissociate in water, resulting in a sharp increase in pH during titration. In contrast, weak acids, like acetic acid (CH₃COOH), only partially dissociate, leading to a more gradual pH change. This difference in dissociation behavior is reflected in the titration curves, where strong acids show a steep slope at the equivalence point, while weak acids exhibit a more gradual slope.
Recommended video:
Weak Acid-Strong Base Titration Curve
pH and Neutralization
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, with lower values indicating acidic conditions and higher values indicating basic conditions. During a titration, the goal is to reach a neutralization point, where the acid and base completely react. The pH at this point can vary depending on whether a strong or weak acid is involved, influencing the shape of the titration curve and the final pH after the addition of the titrant.
Recommended video: