(b) Name three factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
(c) As a reaction proceeds, does the instantaneous reaction rate increase or decrease?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Reaction Rate

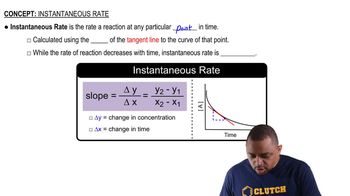
Instantaneous Rate
Reaction Mechanism

(a) What are the units usually used to express the rates of reactions occurring in solution?
b. As the temperature increases, does the reaction rate usually increase or decrease?
Consider the following hypothetical aqueous reaction: A1aq2S B1aq2. A flask is charged with 0.065 mol of A in a total volume of 100.0 mL. The following data are collected: Time (min) 0 10 20 30 40 Moles of A 0.065 0.051 0.042 0.036 0.031 (a) Calculate the number of moles of B at each time in the table, assuming that there are no molecules of B at time zero and that A cleanly converts to B with no intermediates.
Consider the following hypothetical aqueous reaction: A1aq2S B1aq2. A flask is charged with 0.065 mol of A in a total volume of 100.0 mL. The following data are collected: Time (min) 0 10 20 30 40 Moles of A 0.065 0.051 0.042 0.036 0.031 (b) Calculate the average rate of disappearance of A for each 10-min interval in units of M>s.
A flask is charged with 0.100 mol of A and allowed to react to form B according to the hypothetical gas-phase reaction A1g2¡B1g2. The following data are collected: Time (s) 0 40 80 120 160 Moles of A 0.100 0.067 0.045 0.030 0.020 (c) Which of the following would be needed to calculate the rate in units of concentration per time: (i) the pressure of the gas at each time, (ii) the volume of the reaction flask, (iii) the temperature, or (iv) the molecular weight of A?
