b. As the temperature increases, does the reaction rate usually increase or decrease?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Reaction Rate

Temperature and Kinetic Energy

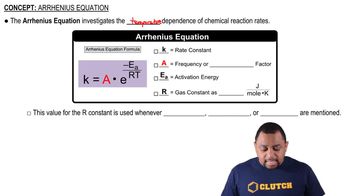
Arrhenius Equation
(b) Name three factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
(a) What are the units usually used to express the rates of reactions occurring in solution?
(c) As a reaction proceeds, does the instantaneous reaction rate increase or decrease?
Consider the following hypothetical aqueous reaction: A(aq) → B(aq). A flask is charged with 0.065 mol of A in a total volume of 100.0 mL. The following data are collected: Time (min) 0 10 20 30 40 Moles of A 0.065 0.051 0.042 0.036 0.031 (a) Calculate the number of moles of B at each time in the table, assuming that there are no molecules of B at time zero and that A cleanly converts to B with no intermediates.
Consider the following hypothetical aqueous reaction: A(aq) → B(aq). A flask is charged with 0.065 mol of A in a total volume of 100.0 mL. The following data are collected: Time (min) 0 10 20 30 40 Moles of A 0.065 0.051 0.042 0.036 0.031 (b) Calculate the average rate of disappearance of A for each 10-min interval in units of M>s.
