The unit cell of a compound containing potassium, aluminum, and fluorine is shown here. (a) What type of lattice does this crystal possess (all three lattice vectors are mutually perpendicular)?
Ch.12 - Solids and Modern Materials

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 12, Problem 33b
Consider the unit cells shown here for three different structures that are commonly observed for metallic elements. (b) Which structure(s) corresponds to the least dense packing of atoms?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the three types of cubic unit cells shown in the image: A (Simple Cubic), B (Body-Centered Cubic), and C (Face-Centered Cubic).
Understand the packing efficiency of each type of cubic unit cell: Simple Cubic (52%), Body-Centered Cubic (68%), and Face-Centered Cubic (74%).
Compare the packing efficiencies to determine which structure has the least dense packing of atoms.
Recognize that the Simple Cubic structure (A) has the lowest packing efficiency at 52%.
Conclude that structure A corresponds to the least dense packing of atoms.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Unit Cell
A unit cell is the smallest repeating unit of a crystal lattice that reflects the overall symmetry and structure of the entire crystal. It defines the arrangement of atoms in a solid and can vary in shape and size. Understanding unit cells is crucial for analyzing the packing efficiency and density of different crystalline structures.
Recommended video:
Guided course
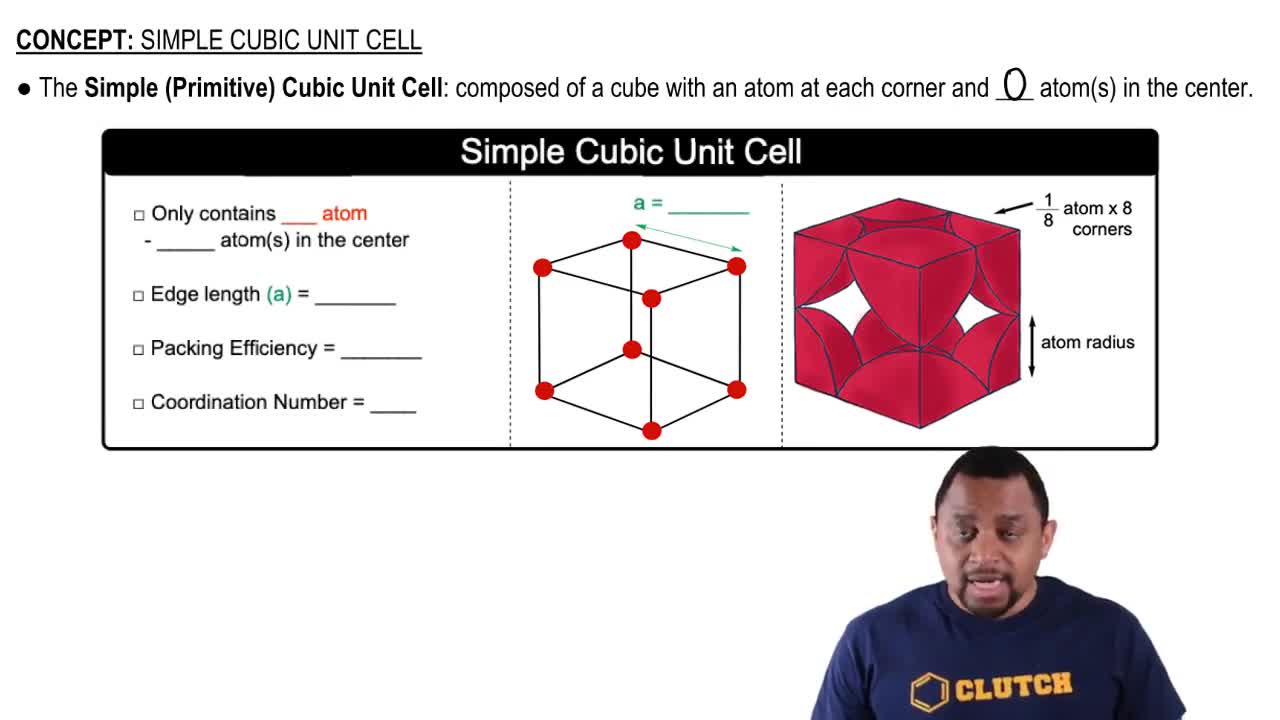
Simple Cubic Unit Cell
Atomic Packing Efficiency
Atomic packing efficiency (APE) refers to the fraction of volume in a crystal structure that is occupied by atoms. It is calculated by comparing the volume occupied by the atoms to the total volume of the unit cell. Structures with higher APE have denser packing, while those with lower APE indicate less dense arrangements, which is essential for determining which structure corresponds to the least dense packing.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Atom Structure
Types of Crystal Structures
Different types of crystal structures, such as face-centered cubic (FCC), body-centered cubic (BCC), and simple cubic (SC), exhibit varying atomic arrangements and densities. Each structure has unique characteristics that influence the physical properties of the material. Identifying these structures helps in understanding their packing efficiency and density, which is key to answering the question about the least dense packing.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Acid Structure and Types
Related Practice
Textbook Question
530
views
Textbook Question
Consider the unit cells shown here for three different structures that are commonly observed for metallic elements. (a) Which structure(s) corresponds to the densest packing of atoms?
459
views
Textbook Question
Sodium metal (atomic weight 22.99 g/mol) adopts a body-centered cubic structure with a density of 0.97 g/cm3. (a) Use this information and Avogadro’s number (NA = 6.022 × 1023/mol) to estimate the atomic radius of sodium. (b) If sodium didn't react so vigorously, it could float on water. Use the answer from part (a) to estimate the density of Na if its structure were that of a cubic close-packed metal. Would it still float on water?
1700
views
1
comments
Textbook Question
Calcium crystallizes in a body-centered cubic structure at 467°C. (a) How many Ca atoms are contained in each unit cell?
1111
views
