Consider the three electronic transitions in a hydrogen atom shown here, labeled A, B, and C. (a) Three electromagnetic waves, all drawn on the same scale, are also shown. Each corresponds to one of the transitions. Which electromagnetic wave (i), (ii), or (iii), is associated with electronic transition C?
The contour representation of one of the orbitals for the n = 3 shell of a hydrogen atom is shown here. (c) In which of the following ways would you modify this sketch if the value of the magnetic quantum number, ml, were to change? (i) It would be drawn larger, (ii) the number of lobes would change, (iii) the lobes of the orbital would point in a different direction, (iv) there would be no change in the sketch.

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Quantum Numbers

Orbital Shapes and Orientation
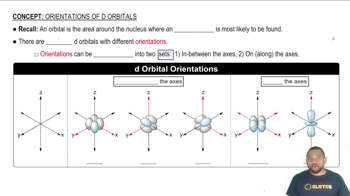
Hydrogen Atom Orbitals

Consider a fictitious one-dimensional system with one electron. The wave function for the electron, drawn below, is c1x2 = sin x from x = 0 to x = 2p. (b) At what value or values of x will there be the greatest probability of finding the electron?
The contour representation of one of the orbitals for the n = 3 shell of a hydrogen atom is shown here. (a) What is the quantum number l for this orbital?
The accompanying drawing shows a contour plot for a dyz orbital. Consider the quantum numbers that could potentially correspond to this orbital. (b) What is the value of the angular momentum quantum number, l?
The accompanying drawing shows a contour plot for a dyz orbital. Consider the quantum numbers that could potentially correspond to this orbital. (c) What is the largest possible value of the magnetic quantum number, ml?
The accompanying drawing shows a contour plot for a dyz orbital. Consider the quantum numbers that could potentially correspond to this orbital. (d) The probability density goes to zero along which of the following planes: xy, xz, or yz?
