At 20 °C (approximately room temperature) the average velocity of N2 molecules in air is 1050 mph. (b) What is the kinetic energy (in J) of an N2 molecule moving at this speed?
Consider the following acid-neutralization reactions involving the strong base NaOH(aq): HNO31aq2 + NaOH1aq2¡NaNO31aq2 + H2O1l2 HCl1aq2 + NaOH1aq2¡NaCl1aq2 + H2O1l2 NH4+1aq2 + NaOH1aq2¡NH31aq2 + Na+1aq2 + H2O1l2 (d) In the third equation NH4 +1aq2 is acting as an acid. Based on the value of H° for this reaction, do you think it is a strong or a weak acid? Explain.

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
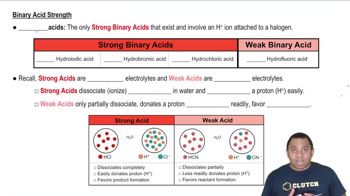
Acid-Base Theory

Strength of Acids
Enthalpy Change (ΔH°)

Suppose an Olympic diver who weighs 52.0 kg executes a straight dive from a 10-m platform. At the apex of the dive, the diver is 10.8 m above the surface of the water. (a) What is the potential energy of the diver at the apex of the dive, relative to the surface of the water?
Suppose an Olympic diver who weighs 52.0 kg executes a straight dive from a 10-m platform. At the apex of the dive, the diver is 10.8 m above the surface of the water. (b) Assuming that all the potential energy of the diver is converted into kinetic energy at the surface of the water, at what speed, in m>s, will the diver enter the water?
Consider two solutions, the first being 50.0 mL of 1.00 M CuSO4 and the second 50.0 mL of 2.00 M KOH. When the two solutions are mixed in a constant-pressure calorimeter, a precipitate forms and the temperature of the mixture rises from 21.5 to 27.7 °C. (a) Before mixing, how many grams of Cu are present in the solution of CuSO4?
