Calculate 3OH-4 and pH for each of the following strong base solutions: (c) 10.0 mL of 0.0105 M Ca1OH22 diluted to 500.0 mL
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria
Chapter 16, Problem 52
Phenylacetic acid 1C6H5CH2COOH2 is one of the substances that accumulates in the blood of people with phenylketonuria, an inherited disorder that can cause mental retardation or even death. A 0.085 M solution of C6H5CH2COOH has a pH of 2.68. Calculate the Ka value for this acid.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acid Dissociation Constant (Ka)
The acid dissociation constant, Ka, quantifies the strength of an acid in solution. It is defined as the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of an acid into its conjugate base and a proton. A higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid, as it dissociates more completely in solution. For weak acids, like phenylacetic acid, Ka can be calculated using the concentrations of the products and reactants at equilibrium.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Characteristics of Ka and Kb
pH and its Relationship to Concentration
pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, calculated as pH = -log[H+]. In the case of weak acids, the pH can provide insight into the degree of dissociation of the acid. For a 0.085 M solution of phenylacetic acid with a pH of 2.68, the concentration of hydrogen ions can be determined, which is essential for calculating the Ka value.
Recommended video:
Guided course
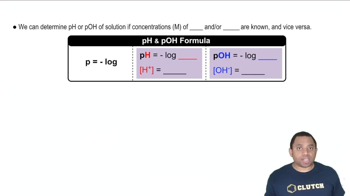
pH and pOH Calculations
Equilibrium Expressions
Equilibrium expressions describe the relationship between the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium. For the dissociation of a weak acid, the expression is given by Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA], where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions, [A-] is the concentration of the conjugate base, and [HA] is the concentration of the undissociated acid. Understanding how to manipulate this expression is crucial for calculating Ka from pH and initial concentrations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Equilibrium Constant Expressions
Related Practice
Textbook Question
349
views
Textbook Question
Calculate the concentration of an aqueous solution of Ca1OH22 that has a pH of 10.05.
473
views
Textbook Question
Write the chemical equation and the Ka expression for the acid dissociation of each of the following acids in aqueous solution. First show the reaction with H+1aq2 as a product and then with the hydronium ion: (a) C6H5COOH
899
views
Textbook Question
A 0.100 M solution of chloroacetic acid 1ClCH2COOH2 is 11.0% ionized. Using this information, calculate 3ClCH2COO-4, 3H+4, 3ClCH2COOH4, and Ka for chloroacetic acid.
771
views
Textbook Question
A 0.100 M solution of bromoacetic acid 1BrCH2COOH2 is 13.2% ionized. Calculate 3H+4, 3BrCH2COO-4, 3BrCH2COOH4 and Ka for bromoacetic acid.
826
views
Textbook Question
If a solution of HF 1Ka = 6.8 * 10-42 has a pH of 3.65, calculate the concentration of hydrofluoric acid.
446
views
