Calculate the pH of each of the following strong acid solutions: (b) 1.52 g of HNO3 in 575 mL of solution
Calculate the concentration of an aqueous solution of Ca1OH22 that has a pH of 10.05.

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
pH and pOH
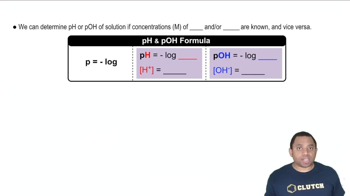
Hydroxide Ion Concentration
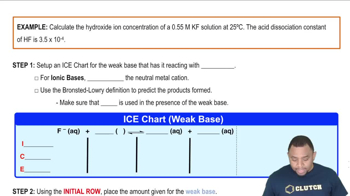
Stoichiometry of Calcium Hydroxide

Calculate the pH of each of the following strong acid solutions: (b) 0.225 g of HClO3 in 2.00 L of solution
Calculate 3OH-4 and pH for each of the following strong base solutions: (c) 10.0 mL of 0.0105 M Ca1OH22 diluted to 500.0 mL
Write the chemical equation and the Ka expression for the acid dissociation of each of the following acids in aqueous solution. First show the reaction with H+1aq2 as a product and then with the hydronium ion: (a) C6H5COOH
Phenylacetic acid 1C6H5CH2COOH2 is one of the substances that accumulates in the blood of people with phenylketonuria, an inherited disorder that can cause mental retardation or even death. A 0.085 M solution of C6H5CH2COOH has a pH of 2.68. Calculate the Ka value for this acid.
A 0.100 M solution of chloroacetic acid 1ClCH2COOH2 is 11.0% ionized. Using this information, calculate 3ClCH2COO-4, 3H+4, 3ClCH2COOH4, and Ka for chloroacetic acid.
