The density of toluene (C7H8) is 0.867 g/mL, and the density of thiophene (C4H4S) is 1.065 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 8.10 g of thiophene in 250.0 mL of toluene. (a) Calculate the mole fraction of thiophene in the solution.
Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following aqueous solutions: (c) 124.0 g of a solution that is 6.45% glucose (C6H12O6) by mass.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
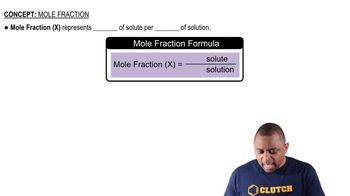
Key Concepts
Percent by Mass

Molar Mass

Moles of Solute
The density of toluene (C7H8) is 0.867 g/mL, and the density of thiophene (C4H4S) is 1.065 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 8.10 g of thiophene in 250.0 mL of toluene. (b) Calculate the molality of thiophene in the solution.
Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following aqueous solutions: (b) 86.4 g of 0.180 m KCl,
Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following solutions: (a) 255 mL of 1.50 M HNO3(aq),
Describe how you would prepare each of the following aqueous solutions, starting with solid KBr: (b) 125 g of 0.180 m KBr,
Describe how you would prepare each of the following aqueous solutions, starting with solid KBr: (d) a 0.150 M solution of KBr that contains just enough KBr to precipitate 16.0 g of AgBr from a solution containing 0.480 mol of AgNO3.
