Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mole Fraction
Mole fraction is a way of expressing the concentration of a component in a mixture. It is calculated by dividing the number of moles of a specific component by the total number of moles of all components in the mixture. In this case, to find the mole fraction of ethanol, you need to determine the moles of ethanol and water in the solution and then use the formula: mole fraction of ethanol = moles of ethanol / (moles of ethanol + moles of water).
Recommended video:
Vapor Pressure
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its liquid or solid phase at a given temperature. It indicates the tendency of a substance to evaporate; higher vapor pressure means a substance evaporates more readily. In this question, the vapor pressures of water and ethanol at 63.5 °C are provided, which are essential for understanding how the components behave in the solution and how they contribute to the overall vapor pressure.
Recommended video:
Raoult's Law and Vapor Pressure
Colligative Properties
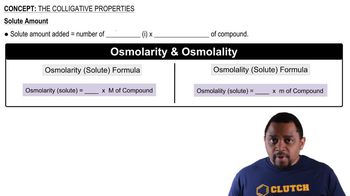
Colligative properties are properties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles in a given amount of solvent, rather than the identity of the solute. These properties include vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and freezing point depression. In this scenario, understanding colligative properties is important because the mixing of water and ethanol will affect the vapor pressure of the solution, which can be analyzed using the mole fractions calculated.
Recommended video: