The electronic structure of a doped semiconductor is shown here. (c) Which region of the diagram represents the band gap?
Silicon is the fundamental component of integrated circuits. Si has the same structure as diamond. (a) Is Si a molecular, metallic, ionic, or covalent-network solid?

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
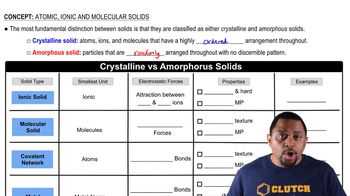
Types of Solids
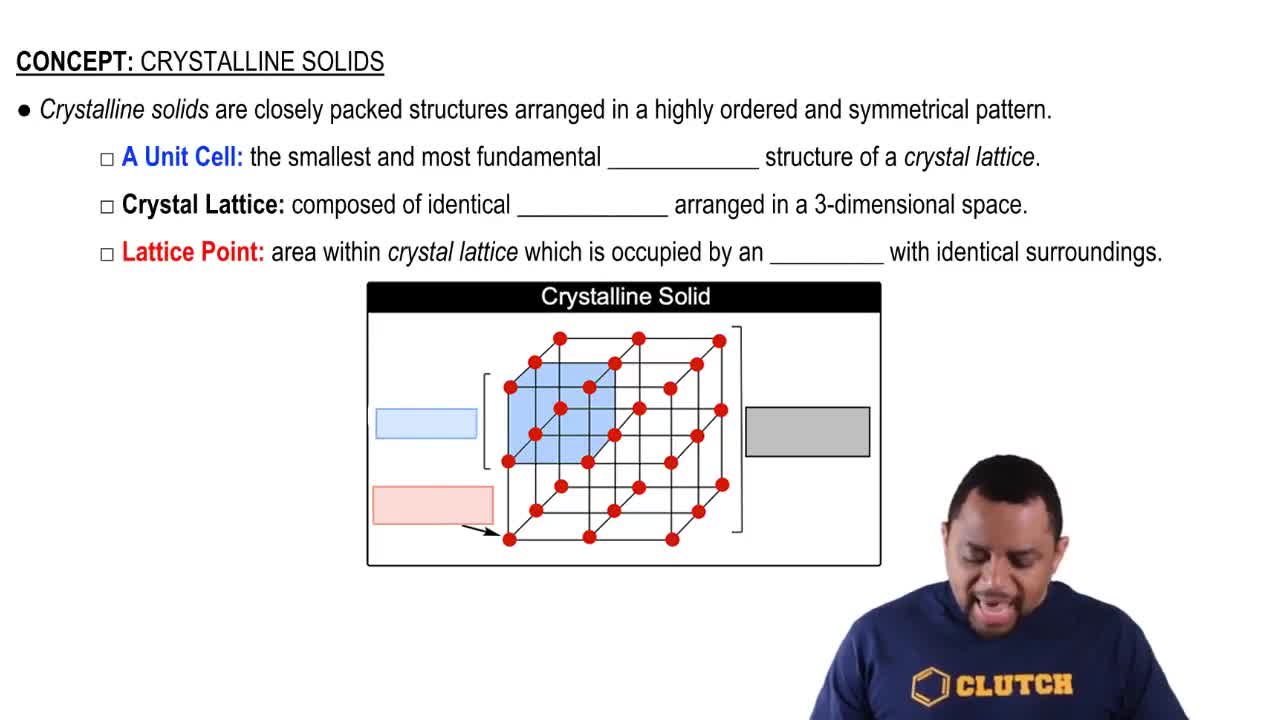
Covalent-Network Solids
Silicon in Electronics

Shown here are cartoons of two different polymers. Which one would have the higher melting point?
The accompanying image shows photoluminescence from four different samples of CdTe nanocrystals, each embedded in a polymer matrix. The photoluminescence occurs because the samples are being irradiated by a UV light source. The nanocrystals in each vial have different average sizes. The sizes are 4.0, 3.5, 3.2, and 2.8 nm. (a) Which vial contains the 4.0-nm nanocrystals?
Silicon is the fundamental component of integrated circuits. Si has the same structure as diamond. (b) Silicon readily reacts to form silicon dioxide, SiO2, which is quite hard and is insoluble in water. Is SiO2 most likely a molecular, metallic, ionic, or covalent-network solid?
What kinds of attractive forces exist between particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) in (a) molecular crystals?
What kinds of attractive forces exist between particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) in (d) and metallic crystals?
