The unit cell of nickel arsenide is shown here. (b) What is the empirical formula?
Consider the unit cells shown here for three different structures that are commonly observed for metallic elements. (b) Which structure(s) corresponds to the least dense packing of atoms?


Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Unit Cell
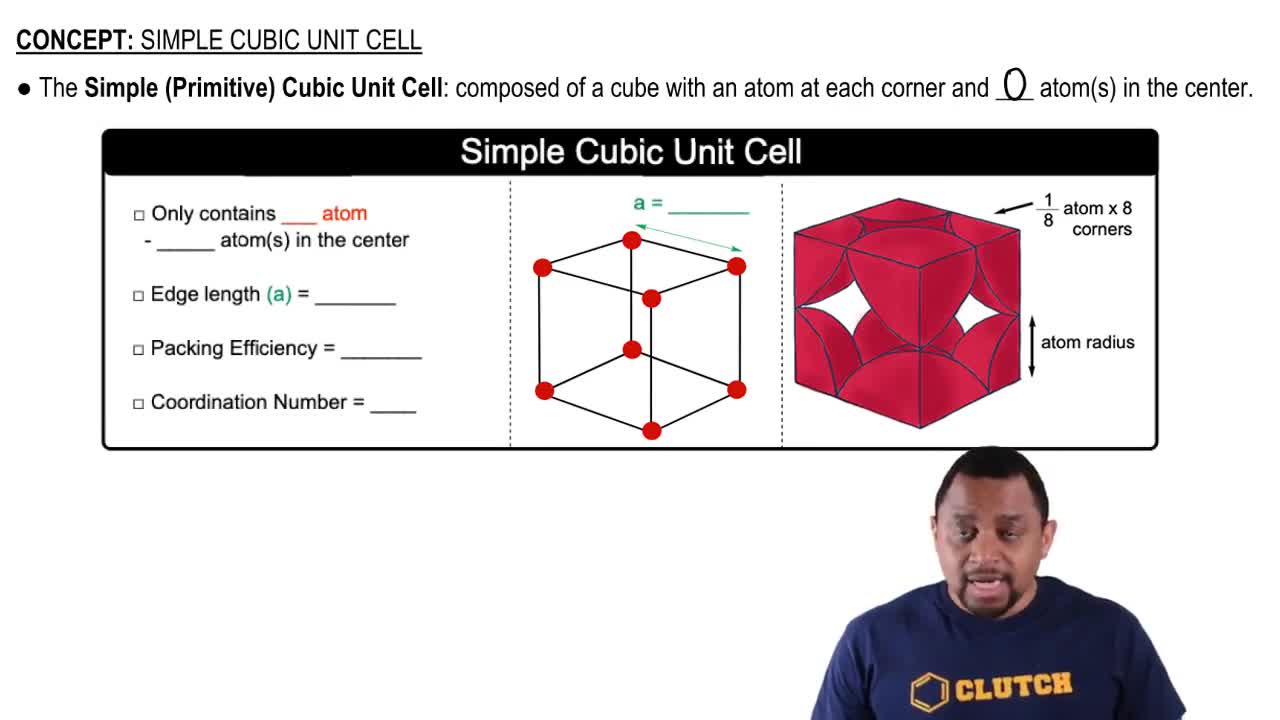
Atomic Packing Efficiency

Types of Crystal Structures

The unit cell of a compound containing potassium, aluminum, and fluorine is shown here. (a) What type of lattice does this crystal possess (all three lattice vectors are mutually perpendicular)?
Consider the unit cells shown here for three different structures that are commonly observed for metallic elements. (a) Which structure(s) corresponds to the densest packing of atoms?
Sodium metal (atomic weight 22.99 g>mol) adopts a body-centered cubic structure with a density of 0.97 g>cm3. (b) If sodium didn't react so vigorously, it could float on water. Use the answer from part (a) to estimate the density of Na if its structure were that of a cubic close-packed metal. Would it still float on water?
Calcium crystallizes in a body-centered cubic structure at 467°C. (a) How many Ca atoms are contained in each unit cell?
