The karat scale used to describe gold alloys is based on mass percentages. (a) If an alloy is formed that is 50 mol% silver and 50 mol% gold, what is the karat number of the alloy? Use Figure 12.18 to estimate the color of this alloy.
(a) What are the C¬C¬C bond angles in diamond?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
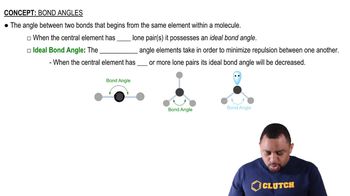
Key Concepts
Tetrahedral Geometry

Bond Angles
Crystal Lattice Structure

The karat scale used to describe gold alloys is based on mass percentages. (b) If an alloy is formed that is 50 mol% copper and 50 mol% gold, what is the karat number of the alloy? What is the color of this alloy?
(c) What atomic orbitals are involved in the stacking of graphite sheets with each other?
Employing the bond enthalpy values listed in Table 8.4, estimate the molar enthalpy change occurring upon (a) polymerization of ethylene. (b) formation of nylon 6,6. (c) formation of polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
Although polyethylene can twist and turn in random ways, the most stable form is a linear one with the carbon backbone oriented as shown in the following figure:
The solid wedges in the figure indicate bonds from carbon that come out of the plane of the page; the dashed wedges indicate bonds that lie behind the plane of the page. (a) What is the hybridization of orbitals at each carbon atom? What angles do you expect between the bonds?
