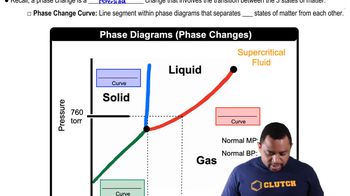
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phase Transition
A phase transition refers to the transformation of a substance from one state of matter to another, such as solid, liquid, or gas. Common examples include melting (solid to liquid) and freezing (liquid to solid). Understanding these transitions is crucial for analyzing changes in physical properties and energy exchanges during the process.
Recommended video:
Phase Changes in Diagrams
Exothermic and Endothermic Processes
Exothermic processes release energy, usually in the form of heat, to the surroundings, while endothermic processes absorb energy from the surroundings. The classification of a phase transition as exothermic or endothermic depends on whether energy is released or absorbed during the transition. For instance, freezing is exothermic as it releases heat.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions Example 2
Freezing of Lava
When molten lava cools and solidifies into rock, it undergoes a phase transition known as freezing. This process is exothermic because the lava releases heat to the environment as it transitions from a liquid state to a solid state. Understanding this transition helps in grasping the geological processes involved in volcanic activity.
Recommended video:
Freezing Point Depression