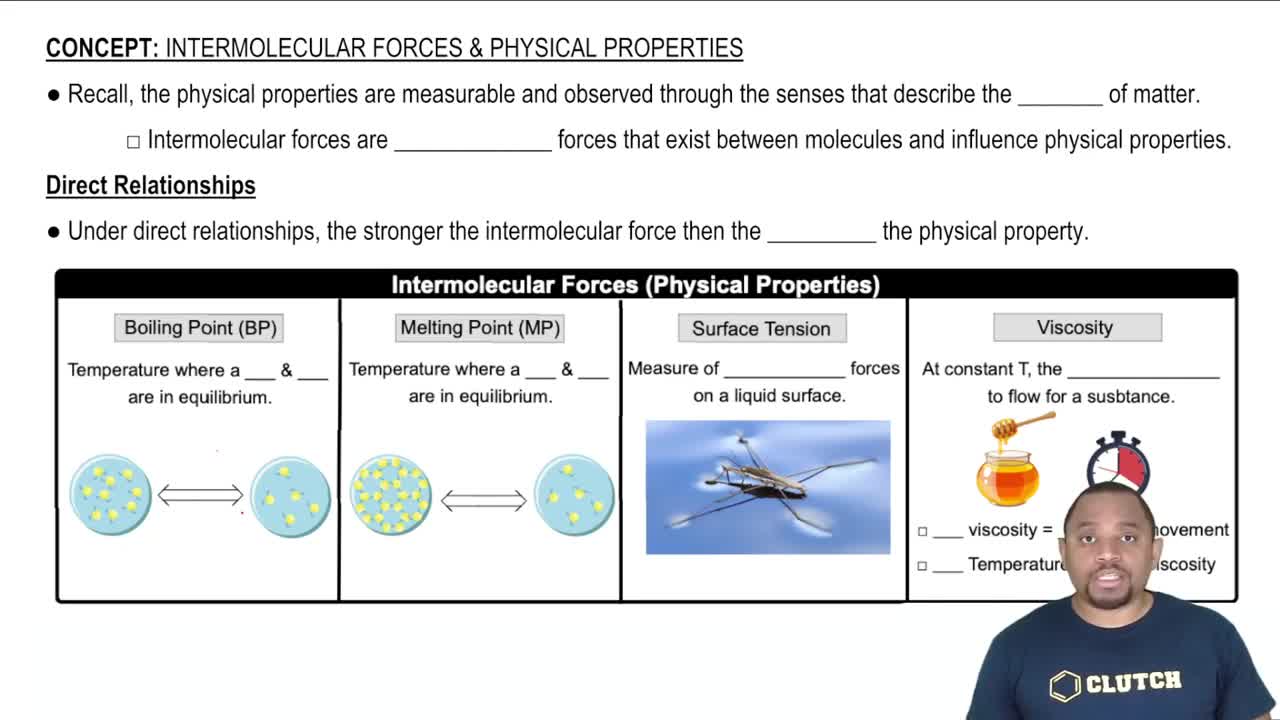
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cohesive Forces
Cohesive forces are the intermolecular forces that hold molecules of the same substance together. In liquids, these forces are responsible for phenomena such as surface tension, where the molecules at the surface experience a net inward force due to stronger interactions with neighboring molecules. Understanding cohesive forces is essential for predicting how a liquid behaves on different surfaces.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular Forces and Properties
Adhesive Forces
Adhesive forces are the attractive forces between molecules of different substances. When a liquid comes into contact with a surface, adhesive forces determine how well the liquid spreads or wets the surface. In the case of water on a nonpolar surface, the adhesive forces are typically weaker than the cohesive forces, leading to minimal wetting and the formation of droplets.
Recommended video:
Types of Intermolecular Forces
Wetting and Contact Angle
Wetting refers to the ability of a liquid to maintain contact with a solid surface, influenced by the balance of cohesive and adhesive forces. The contact angle is a measure of this wetting; a smaller angle indicates better wetting. On nonpolar surfaces, water tends to form a larger contact angle, indicating poor wetting, which is crucial for interpreting the diagrams in the question.
Recommended video: