Based on their composition and structure, list CH2Cl2, CH3CH2CH3, and CH3CH2OH in order of (c) increasing surface tension
Name the phase transition in each of the following situations and indicate whether it is exothermic or endothermic: (c) Rubbing alcohol in an open container slowly disappears.

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Evaporation
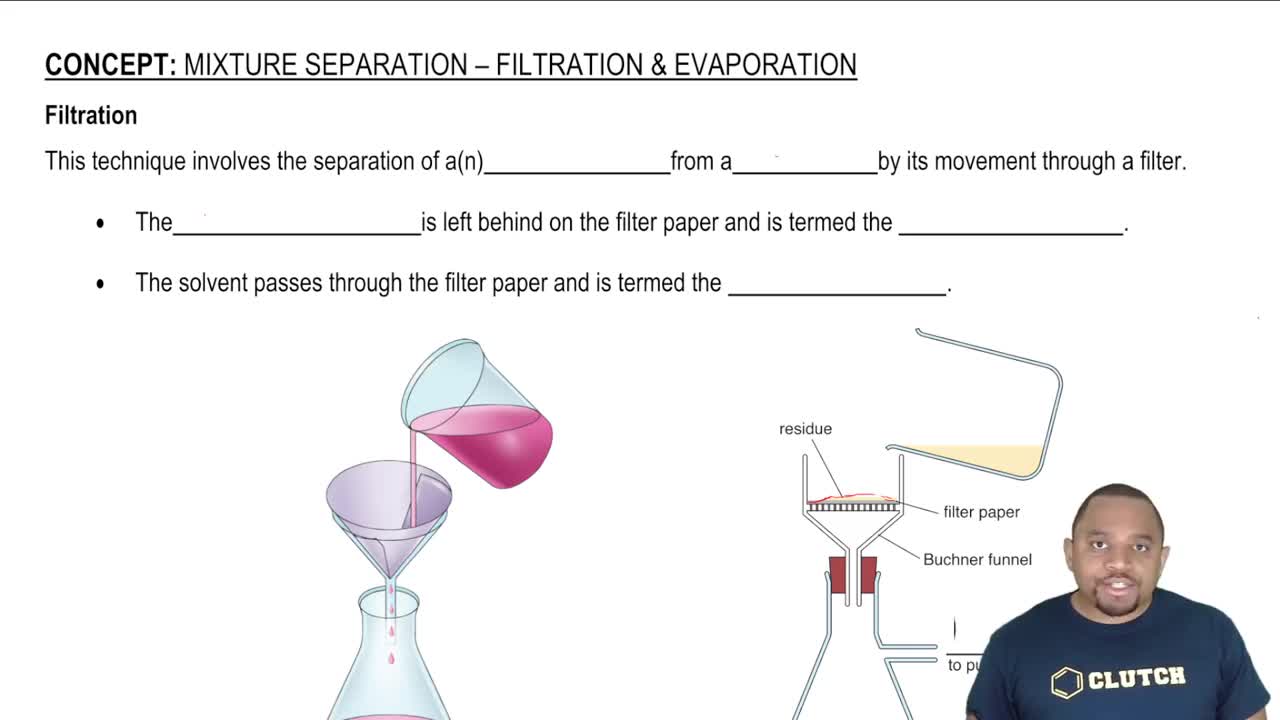
Endothermic Processes

Intermolecular Forces

Liquids can interact with flat surfaces just as they can with capillary tubes; the cohesive forces within the liquid can be stronger or weaker than the adhesive forces between liquid and surface:
(b) Which of these diagrams, i or ii, rep- resents what happens when water is on a nonpolar surface?
Name the phase transition in each of the following situations and indicate whether it is exothermic or endothermic: (d) Molten lava from a volcano turns into solid rock.
Ethyl chloride (C2H5Cl) boils at 12 °C. When liquid C2H5Cl under pressure is sprayed on a room-temperature (25 °C) surface in air, the surface is cooled considerably. (a) What does this observation tell us about the specific heat of C2H5Cl(g) as compared with that of C2H5Cl(l)?
Ethyl chloride (C2H5Cl) boils at 12 °C. When liquid C2H5Cl under pressure is sprayed on a room-temperature (25 °C) surface in air, the surface is cooled considerably. (b) Assume that the heat lost by the surface is gained by ethyl chloride. What enthalpies must you consider if you were to calculate the final temperature of the surface?
