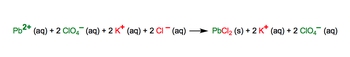
In this example question it says convert the following molecular equation into a complete ionic equation. So here we have 3 moles of calcium bromide aqueous reacting with two moles of lithium phosphate aqueous producing 6 moles of lithium bromide as an aqueous compound plus one mole of calcium phosphate solid.
All right, so remember we can only break up aqueous compounds, so only these three compounds will break up. If you are solid, a liquid, or gas, you will not break up in the complete ionic equation. Also remember that the coefficient gets distributed to each one of these compounds.
Now what exactly does that mean? Well, here that means that this three is going to get distributed to the number of calciums and the number of bromines. So it gets distributed to California and branch when this breaks up into its ions, we know that we're going to have calcium ion aqueous plus bromide ion aqueous, then we distribute the coefficient.
So that's going to give us three calcium ions and then this is 3 * 2 six bromide ions. Plus also remember that when we have an ion, it's an aqueous phase within a solution. This two is going to get distributed to here and to here. So we know that's going to give us 6 lithium ions because it is 2 * 3 + 2 phosphate ions.
Remember phosphate is a polyatomic ion, produces 6 gets distributed to lithium and bromide. So 6 lithium plus one ions +6 bromide ions. This is a solid so it stays together. Does not break up into ions so plus one, so one. Not 6/1 calcium phosphate solid O. This here represents our complete ionic equation.
Remember to break up only aqueous compounds, and remember to distribute the ions to each one of well. Distribute the number of coefficients to each one of those ions that you form.