Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quantum Numbers
Quantum numbers are a set of numerical values that describe the unique quantum state of an electron in an atom. The principal quantum number (n) indicates the energy level, while the magnetic quantum number (ml) specifies the orientation of the orbital in space. Understanding these numbers is crucial for predicting the shape and orientation of atomic orbitals.
Recommended video:
Orbital Shapes and Orientation
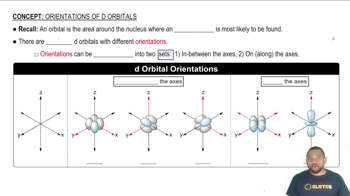
Atomic orbitals have distinct shapes and orientations based on their quantum numbers. The shape of an orbital is determined by the angular momentum quantum number (l), while the orientation is influenced by the magnetic quantum number (ml). Changes in ml can lead to different orientations of the lobes of the orbital, affecting how they are represented in sketches.
Recommended video:
Hydrogen Atom Orbitals
In a hydrogen atom, the orbitals are defined by solutions to the Schrödinger equation, which describe the probability distribution of an electron. For the n = 3 shell, there are multiple orbitals (3s, 3p, 3d) with varying shapes and orientations. Understanding these orbitals helps in visualizing how changes in quantum numbers affect their representation.
Recommended video: