What is a hormone-response element? a. a receptor for a steroid hormone b. a receptor for a polypeptide hormone c. a segment of DNA where a hormone–receptor complex binds d. an enzyme that is activated in response to hormone binding and produces a second messenger
Compare and contrast the modes of action of lipid-soluble and water-soluble hormones.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
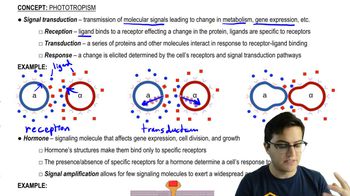
Key Concepts
Lipid-Soluble Hormones

Water-Soluble Hormones

Signal Transduction
Which of the following assertions regarding hormones is correct? Select True or False for each statement. T/F Growth and metamorphosis are controlled by hormones. T/F Cortisol stimulates the production of ACTH. T/F Hormones produced by the hypothalamus are considered neurohormones. T/F Hormonal changes during puberty and pregnancy are forms of endocrine disruption.
True or False: In hormone systems, negative feedback occurs when the presence of a hormone inhibits release of the hormone.
Why is the observation that one hormone may bind to more than one type of receptor important?
Compare and contrast the structure and function of the anterior and posterior pituitary glands.
Design a study to test the hypothesis that the symptoms of jet lag are caused by disruption of normal daily cortisol rhythms.
