What do some photosynthetic bacteria use as a source of electrons instead of water? a. oxygen (O2) b. hydrogen sulfide (H2S) c. organic compounds (e.g., CH3COO−) d. nitrate (NO3-)
Unlike plant cell walls that contain cellulose, bacterial cell walls are composed of .
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Bacterial Cell Wall Composition

Peptidoglycan Structure
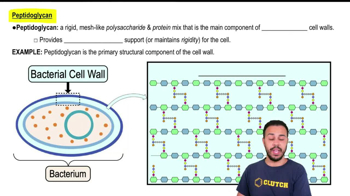
Differences Between Plant and Bacterial Cell Walls

What does the chemiosmotic hypothesis claim? a. ATP is generated using phosphates taken from intermediates in the electron transport chain. b. ATP is generated using a phosphate gradient produced by glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. c. ATP is generated using a proton-motive force that is produced by the electron transport chain. d. Water is generated using electrons taken from NADH and FADH2 and transported through the electron transport chain.
What are organisms called that use inorganic compounds as electron donors in cellular respiration? a. phototrophs b. heterotrophs c. organotrophs d. lithotrophs
Explain how feedback inhibition regulates metabolic pathways.
Evaluate these statements about Koch's postulates, which are used to establish a causative link between a specific microbe and a specific disease. Select True or False for each statement. T/F The microbe must be present in individuals suffering from the disease and absent from healthy individuals. T/F The microbe must be isolated and grown in pure culture. T/F If organisms from the pure culture are injected into a healthy experimental animal, the disease symptoms should appear. T/F The microbe does not have to be isolated from the experimental animal as long as the disease is present.
What has metagenomic analysis allowed researchers to do for the first time? a. sample organisms from an environment and grow them under defined conditions in the lab b. isolate organisms from an environment and sequence their entire genome c. study organisms that cannot be cultured (grown in the lab) d. identify important morphological differences among species
