Choose the best definition of a fossil. a. a rock that contains information about an organism b. a bone, tooth, shell, or other hard part of an organism that has been preserved c. any trace of an organism that lived in the past d. any part of a dead organism
Which of the following best characterizes an adaptive radiation? a. Descendant species occupy a large geographic area. b. A single lineage diversifies rapidly, and descendant species occupy many habitats and ecological roles. c. Natural selection is particularly intense, because disruptive selection occurs. d. Species recover after a mass extinction.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Adaptive Radiation
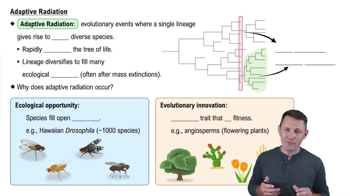
Natural Selection

Ecological Roles

Why does the presence of extinct forms and transitional features in the fossil record support the pattern component of the theory of evolution by natural selection? Select True or False for each statement. T/F It supports the hypothesis that individuals change over time. T/F It supports the hypothesis that weaker species are eliminated by natural selection. T/F It supports the hypothesis that species evolve to become more complex and better adapted over time. T/F It supports the hypothesis that species change over time.
Critique the following statement: The absence of a trait cannot be used as a synapomorphy in phylogenetic analysis; only shared derived traits that are present in the clade can be used.
Which of the following is an example of homoplasy? a. hair in humans and fur in mice b. astragalus ankle bones in hippos and deer c. Hox genes in humans and flies d. streamlined bodies in dolphins and ichthyosaurs
What important assumption does parsimony make when assessing which phylogenetic tree is most accurate? Why was parsimony misleading in the case of the astragalus during the evolution of artiodactyls?
You can use a 'one-snip test' to identify monophyletic groups—meaning that if you 'cut' any branch on a tree, everything that 'falls off' is a monophyletic group. Why is this valid?
