Which of the following actions correctly describe a role performed by at least one type of intercellular connection? Select True or False for each statement. T/F Allows communication between adjacent cells. T/F Forms a watertight barrier between the cells. T/F Uses components of the extracellular matrix to indirectly connect adjacent cells. T/F Associates with cytoskeletal components to resist pulling forces.
Ch. 11 - Cell-Cell Interactions
Chapter 11, Problem 4
What does it mean to say that a signal is transduced? a. The signaling molecule enters the cell directly and elicits a cellular response. b. The signal is generated by the production of proteins. c. The physical form of the signal changes between the outside of the cell and the inside. d. The signal is amplified.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the term 'transduced'. In the context of cell signaling, transduction refers to the process by which a signal is converted from one form to another. This usually involves a series of steps, known as a signal transduction pathway, where the signal is passed along from one molecule to another, often with an amplification of the signal.
Step 2: Evaluate each option in relation to the definition of transduction. Option a suggests that the signaling molecule enters the cell directly and elicits a response. This is not necessarily transduction, as it doesn't involve a change in the form of the signal.
Step 3: Option b suggests that the signal is generated by the production of proteins. This is not transduction, as it refers to the generation of a signal, not the conversion or change in form of a signal.
Step 4: Option c suggests that the physical form of the signal changes between the outside of the cell and the inside. This is a good description of transduction, as it involves a change in the form of the signal.
Step 5: Option d suggests that the signal is amplified. While amplification can be a part of transduction, it is not the defining feature. Therefore, the best answer is option c.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction refers to the process by which a cell converts an external signal into a functional response. This involves a series of molecular events, often initiated by the binding of a signaling molecule (ligand) to a receptor on the cell surface, leading to changes in cellular activity. Understanding this concept is crucial for grasping how cells communicate and respond to their environment.
Recommended video:
Guided course
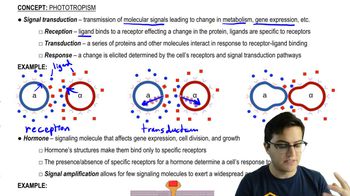
Signal Transduction and Response
Signal Amplification
Signal amplification is a key aspect of signal transduction where a small initial signal can lead to a large cellular response. This is often achieved through a cascade of biochemical reactions, where each step activates multiple downstream molecules, thereby magnifying the effect of the original signal. This concept highlights the efficiency and sensitivity of cellular communication.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Signal Amplification
Signal Modality Change
The concept of signal modality change refers to the transformation of a signal's physical form as it moves from the extracellular environment to the intracellular space. For instance, a chemical signal outside the cell may be converted into an electrical signal or a different biochemical form inside the cell, allowing for appropriate cellular responses. This transformation is essential for effective communication within the cell.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Signal Amplification
Related Practice
Textbook Question
606
views
Textbook Question
Summarize the experimental evidence in sponges showing that animal cells adhere to each other selectively. Explain the molecular basis of selective adhesion.
603
views
Textbook Question
Suppose you were to model amplification by the phosphorylation cascade in Figure 11.16, using a penny for each kinase 1, a nickel for each kinase 2, and a dime for each kinase 3. Also suppose that Ras and each of the kinases can activate 10 proteins. How much money would you need to construct your model?
352
views
Textbook Question
What is the significance of the observation that many signal transduction pathways create a network, where they intersect or overlap?
509
views
